Welcome to our website! Call Us: +86-18622194621 E-mail: toptac@fancyco.com
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-12 Origin: Site

approximate proportion by weight
Material/Component | Approximate Proportion by Weight (%) |
|---|---|
Lead and lead components | 76 |
Sulfuric Acid (Electrolyte) | 22 |
Antimony | 2 |
lead dioxide and sponge leadlithium compounds and carbon
Lead-acid batteries have lead dioxide on the positive plate. They have sponge lead on the negative plate. These help store and give out energy well.
Sulfuric acid is the electrolyte in the battery. It helps chemical reactions happen. It also lets ions move to make power.
Separators keep the plates apart in the battery. This stops short circuits. They let ions move through safely.
The battery case is made of strong polypropylene plastic. It protects the inside parts. It also stops leaks.
Lead-acid batteries cost less and are good for storing energy. They are easy to recycle and work well. But they hold less energy than lithium-ion batteries. They also need more care.

lead dioxidesponge lead
Positive Plate (Cathode):
lead
Negative Plate (Anode):
tiny holes
carbon-based materials
The electrolyte does more than just sit in the battery. It helps store and release energy, so it is very important.
Modern separators use plastics like polyethylene. These plastics do not break down in acid. The separator’s tiny holes block things that could cause shorts. Its design helps ions move easily.
Note: The separator must be strong, stable, and work well with the electrolyte. This keeps the battery safe and working right.
Component | Material/Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
Battery Case | Polypropylene or hard rubber | Protects internal parts and provides support |
The case must be tough and stop leaks. Battery manufacturing uses strong plastics to keep batteries safe and working for a long time.
Terminals link the battery to other devices. They must carry electricity well and not rust from the electrolyte.
Material | Conductivity | Corrosion Resistance | Strength | Cost | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Lead | Moderate | High | Low | Low | Lead-acid batteries |
Brass | High | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | High-performance batteries |
Copper | Excellent | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate to High | Industrial, marine |
Steel | Low | Moderate | High | Low | Some industrial |
Silver/Gold-Plated | Very High | High | Moderate | High | High-end electronics, racing |
Beryllium Copper | Good | Excellent | High | High | Springs, connectors, aerospace |
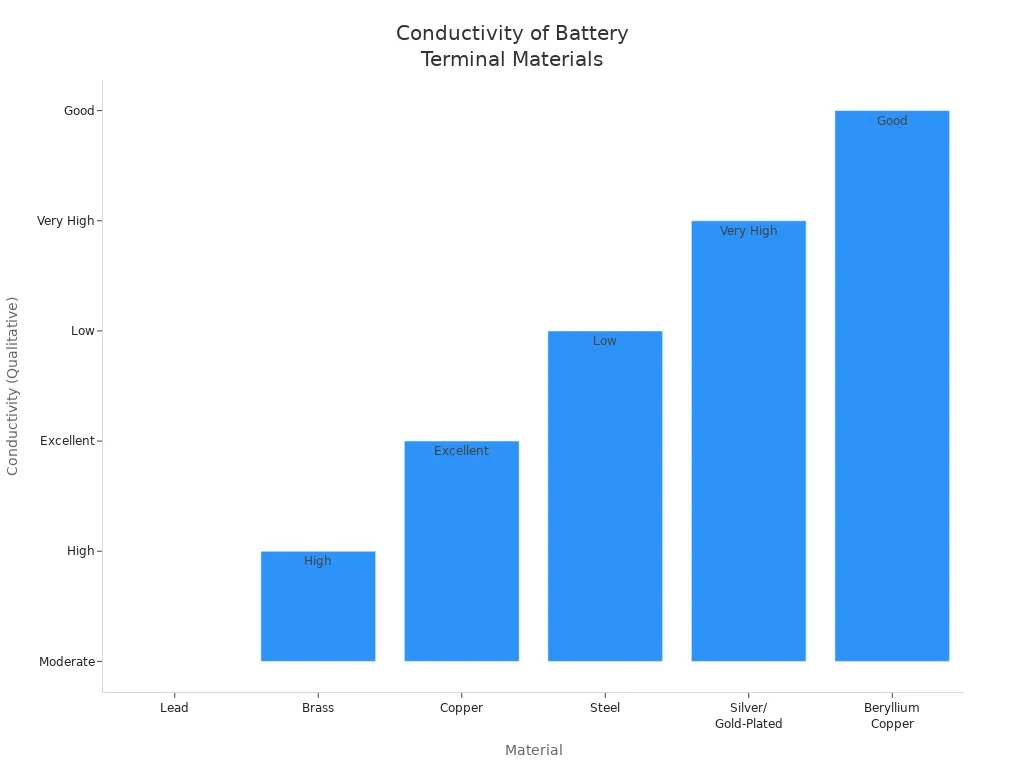
Lead is the most used terminal material in lead-acid batteries. It does not rust from the electrolyte. Brass and copper are used for special needs. They give better conductivity or strength.
Good terminals help the battery work safely and well. Battery manufacturing adds coatings to stop rust and make terminals last longer.
All these battery materials components—electrodes, electrolyte, separator, case, and terminals—work together to give power. Their design comes from years of research in battery manufacturing and electrochemical materials.
lead dioxide at the cathode and sponge lead at the anodeIons move between the cathode and anode
The cathode uses lead dioxide. Lead dioxide is dark brown and rough. It reacts with sulfuric acid when the battery is used. It takes in electrons and forms lead sulfate and water. When charging, lead sulfate turns back into lead dioxide. The cathode must handle many cycles of this reaction. Its strong build helps the battery last longer and work well.
The anode uses sponge lead. Sponge lead looks gray and has many tiny holes. This texture gives it a big surface area. When the battery is used, the anode reacts with sulfate ions from the acid. It forms lead sulfate and gives off electrons. When charging, lead sulfate turns back into sponge lead. The anode’s holes help the battery store and give out energy fast.
The way the cathode and anode are made lets the battery be used, charged, and used again many times.
Aspect | Lead-Acid Battery | Lithium-Ion Battery |
|---|---|---|
Electrode Materials | Lead (anode), Lead dioxide (cathode) | Lithium compounds (cathode), Graphite or carbon-based anode |
Electrolyte | Sulfuric acid | Lithium salt in organic solvent |
Energy Density | Lower; heavier and bulkier for same capacity | Higher; lighter and more compact packs |
Cycle Life | 300–500 cycles | Hundreds to thousands of cycles |
Lithium-ion batteries use lithium compounds for the cathode. They use graphite or carbon for the anode. These materials give lithium-ion batteries more energy and longer life. The cathode and anode in lithium-ion batteries also let them charge faster and be lighter. But lead-acid batteries are still used a lot. They are cheap and work well.
sulfuric acid reacts with the plates
The amount of acid changes when the battery is used or charged. More acid means the battery is charged. Less acid means the battery is low. The electrolyte helps store energy. It also shows if the battery is charged or not.
Component | Role in Charge/Discharge Cycle | Key Properties and Functions |
|---|---|---|
Electrolyte | Moves ions between plates and helps reactions happen. It lets the battery change between lead and lead sulfate. | Sulfuric acid solution; lets ions move; changes show charge level. |
separator sits between the plates
The separator:
Keeps the plates apart.
Lets ions move through.
Stops short circuits and dendrites.
lithium salt in a liquid
Component | Lead-Acid Batteries | Lithium-Ion Batteries |
|---|---|---|
Electrolyte | Sulfuric acid, liquid or gel | Lithium salt in a liquid |
Separator | Absorbs liquid or is a gel | Thin plastic sheet |
Function | Holds liquid, keeps plates apart | Moves lithium ions, keeps electrodes apart |
Safety/Design Considerations | Has a valve for pressure control | Stops dendrites, keeps battery safe |
The electrolyte and separator work together. They help batteries store energy safely and well.

polypropylenelead-acid case with lithium iron phosphate
Material | Application | Key Properties Contributing to Safety and Durability |
|---|---|---|
Polypropylene | Lead-acid car batteries | Lightweight, highly resistant to chemicals and battery acid, durable under rough handling conditions |
Polypropylene is the best material for battery cases. It works well in hard conditions. It also helps the battery last longer by stopping rust and damage.
lead alloybrass
Material | Electrical Conductivity | Corrosion Resistance | Typical Use/Environment |
|---|---|---|---|
Lead Alloy | Excellent conductivity | Minimal corrosion | Common in lead-acid batteries |
Brass | High conductivity | High corrosion resistance | Marine and harsh environments |
Copper | Exceptional conductivity | Tin-plated to resist corrosion | High-performance applications |
Tin-Coated Brass | Combines brass strength and tin corrosion resistance | Ideal for marine and industrial settings | Marine and industrial environments |
Good terminal materials help batteries work safely and last longer. Battery makers add coatings to make terminals stronger.
Modern lead-acid batteries have many safety features. These features protect people and equipment from danger.
Fire detection systems use smoke, heat, and gas sensors to find problems fast.
Fire suppression systems put out fires quickly with clean sprays or water mist.
Ventilation systems remove hydrogen gas made during charging.
Sprinkler systems help control fires but must be used carefully near electricity.
Portable fire extinguishers are nearby, and workers know how to use them.
These safety features work together to keep batteries safe. They help stop leaks, explosions, and other problems.
cheap and work well
Lead-acid batteries are often used to store solar power at homes and businesses. People save extra solar energy to use later.
Power companies use these batteries for backup power and to help balance the grid. They also use them to lower peak energy use.
Data centers, telecom towers, and factories use lead-acid batteries for backup during blackouts.
New types like VRLA, AGM, and gel batteries are safer and last longer.
easy to recyclework welltrust them for storing electricity
table below shows how they are different
Feature | Lead-Acid Battery | Lithium-Ion Battery |
|---|---|---|
Energy Density | Lower (approx. 1.2 kWh per 100Ah) | Higher (approx. 2.4 kWh per 100Ah) |
Weight (100Ah) | Heavier (60-70 pounds) | Lighter (30-40 pounds) |
Cycle Life | Shorter (200-300 cycles) | Longer (2000-5000 cycles) |
Maintenance | Needs regular care | No maintenance needed |
Usable Discharge Depth | About 50% | 80-100% |
Charging Time | Slower (8-16 hours) | Faster (2-4 hours) |
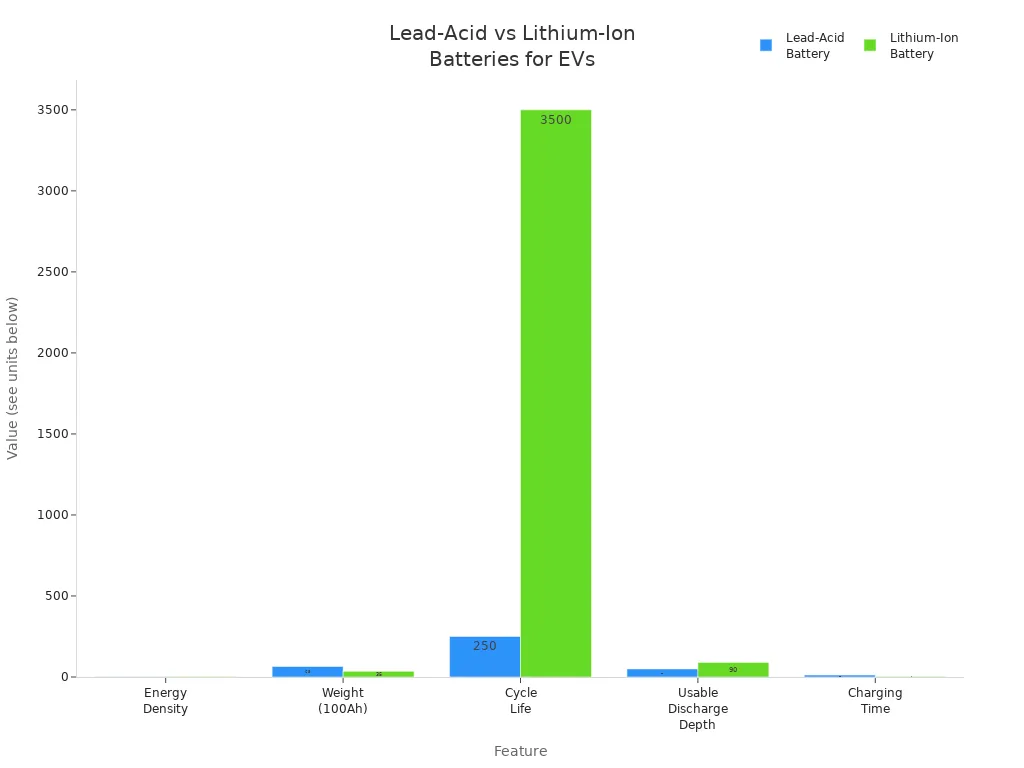
Lithium batteries use new materials and can store more energy in a smaller size. They last longer and charge much faster. Lead-acid batteries are still used to start cars and in some electric vehicles when price is important. For new energy storage, lithium batteries are the top choice, but lead-acid batteries are still used in many places.
lead dioxide on the positive plateSulfuric acid is used as the electrolyte
Sulfuric acid is important for the battery. It helps store and release energy. The acid reacts with the plates when charging or discharging. This reaction makes the battery give power.
Terminals are where you attach cables. They let electricity flow out of the battery. Most terminals are made from lead alloy. This material lets electricity move well.
Lead-acid batteries have safety features. They have strong cases and vents. These stop leaks and control gas. Using the battery the right way keeps it safe.