Welcome to our website! Call us: +86-18622194621 E-mail: toptac@fancyco.com
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-11-04 Origin: Site

In 2021, polyethylene made up about 46.55% of the battery separator market. This shows it is more popular than other materials.
The melting point is important for battery safety. When the temperature hits 130°C, the PE separator turns nonporous. It stops ions from moving. This lowers the chance of overheating.
Separator Type | Melting Point (°C) | Safety Feature |
|---|---|---|
PE | 130 | Turns into nonporous film and stops ions from moving |
PP | 165 | Keeps its shape to help stop short circuits |
Knowing this helps you and makers pick safer battery designs.
The PE separator melts at 130°C to 135°C. This is very important for battery safety. It stops ions from moving. This helps prevent the battery from getting too hot.
PE separators are used in many batteries. They make up about 46.55% of the market. They are strong and stable. They help batteries work better.
When the PE separator melts, it works like a safety switch. It blocks ions from moving. This stops the battery from getting too hot. It also lowers the chance of fire.
Picking the right separator is important. PE separators shut down fast. PP separators can handle higher heat but react slower.
Always use batteries at safe temperatures. If a battery feels hot, stop using it right away. This helps prevent accidents.
You might wonder why a PE separator is important in batteries. A PE separator is a thin film made from polyethylene. It sits between the positive and negative electrodes. This film keeps them from touching. That helps stop short circuits. The separator has tiny pores all over. These pores let ions move through easily. This helps the battery work better.
Polyethylene makes the separator strong and stable. That is why many manufacturers use it. The separator’s pores help the electrolyte spread and ions move. This means the battery can give power more easily.
Here are some main properties of polyethylene that make it good for separators:
It is a thermoplastic polymer with strong mechanical strength.
The separator has lots of pores, which helps conductivity when wet.
It is cheap and stays stable in tough chemical conditions.
You can see common features of PE separators in the table below:
Property | Value |
|---|---|
Thickness | 9 μm |
Median Pore Size | 132 nm |
Percent Porosity | 40% |
You need the separator to keep your battery safe and working well. In big lead-acid batteries, the separator stops short circuits from sharp edges. Its strong design protects the battery during use and making.
The separator’s even pores and low resistance let ions flow easily. This helps the battery give strong power and last longer. The separator also stands up to strong acids and tough chemicals. That keeps your battery stable for a long time.
In car and industrial batteries, the separator helps keep power steady. It helps the battery start in cold weather and works in hard conditions. You can trust the separator to block ions if the battery gets too hot. This safety feature shuts down the cell and stops overheating.
You can see the separator does more than just separate. It is a key part of batteries, making them safer and better.
It is important to know the melting point of a PE separator. Most polyethylene separators melt between 130°C and 135°C. This temperature is much higher than how hot batteries usually get. Batteries normally work below 60°C. The separator stays strong and does its job when the battery is used. If the temperature gets close to the melting point, the separator starts to change.
Here is a table that shows how different separator materials melt and what they do:
Material Type | Melting Point (°C) | Functionality |
|---|---|---|
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) | ∼110 | Shuts down fast at 110°C, blocks ions to stop reactions |
Polyethylene (PE) | 130–135 | Turns nonporous at 130°C, stops ions, prevents overheating |
You can see PE separators melt at a higher temperature than LDPE. This makes PE safer for batteries that need more protection.
When the battery gets hotter, the PE separator changes. At about 130°C, the separator starts to lose its shape. This means it cannot stay the same size and begins to shrink. If the temperature goes up to 135°C, the separator melts. At this point, it cannot work as a barrier anymore.
If the temperature reaches 140°C or more, the separator melts all the way. It shrinks and can disappear between the electrodes. This can cause a short circuit, which is very dangerous.
Here is a table that shows what happens to the PE separator at different temperatures:
Temperature (°C) | Effect on PE Separator |
|---|---|
105–120 | Loses shape, gets weaker |
130 | Starts melting, risk of short circuits |
135 | Melting point, separator is unstable |
140 | Fully melted, shrinks, high danger |
The melting process helps keep batteries safe. When the separator melts, it blocks ions from moving. This stops the battery and helps prevent overheating or fire. But if the temperature goes past the melting point, the separator cannot protect the battery anymore.
Tip: Always use batteries at safe temperatures. If a battery feels hot, stop using it right away.
Manufacturers test PE separators to make sure they are safe. They heat the separator to different temperatures like 120°C, 150°C, and even 250°C. They also check how the separator changes from 20°C to 280°C. These tests help make sure the separator works well in real batteries.
The melting point of the PE separator is very important for battery design. A separator with the right melting point helps keep your battery safe.
Battery cell separators help keep your devices safe. Their job gets more important when things get hot. As the battery heats up, the PE separator melts. When this happens, the separator changes from having tiny holes to being solid. This new layer stops ions from moving. The battery stops working because ions cannot pass. This is called shutdown. Shutdown works like a safety switch inside the battery.
Shutdown separators use materials with different melting points. For example, a PE–PP double-layer separator shuts down at about 130°C. It melts again at 165°C. This gives a safety window. The lower melting point helps the separator react fast to heat. The higher melting point keeps it strong during normal use.
Here is a table that shows how shutdown works inside the battery:
Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Mechanism | The membrane with tiny holes turns into a solid layer as it gets hot. |
Function | Stops ions from moving and keeps the battery from getting too hot. |
Materials Involved | Uses two materials with different melting points. |
Safety Window Temperature | Shows the difference between the two melting points. |
Example | PE–PP double-layer separator shuts down at about 130°C and melts at about 165°C. |
Importance of Fusible Substance | A lower melting point makes the separator react faster to heat and gives a bigger safety window. |
Shutdown separators are very important for batteries. They help stop overheating and keep batteries safe. The shutdown process blocks ions and stops the battery before it gets too hot.
Shutdown separators protect you from thermal runaway. Thermal runaway happens when the battery gets too hot and cannot stop heating up. The separator melts and lets the electrodes touch. This can make the battery catch fire or even explode.
Shutdown separators block ions when it gets too hot. This stops the battery from heating up more. Batteries with shutdown separators fail less often.
Safety reports show that batteries with very thin separators, like 24µm or less, have more problems with dirt or other things inside. Batteries with lots of power can catch fire if stressed. Separator problems can cause these failures. If the separator melts, it can cause a short circuit inside the battery. You need to know how separators work to stay safe.
Note: If your battery feels hot or gets bigger, stop using it. Shutdown separators help, but you should always follow safety rules.
Shutdown separators lower the chance of battery fires and explosions. Tests show that the SRL (separator rapid layer) stops current during short circuits or when it gets too hot. This helps stop thermal runaway. Impact tests show the SRL lowers battery explosions by 53%. The SRL also blocks too much current, which stops more heat from building up in broken batteries.
Here is a table that shows how shutdown separators make batteries safer:
Evidence Description | Outcome |
|---|---|
The SRL stops current during short circuits or when it gets too hot. | Stops thermal runaway. |
The SRL lowers battery explosions by 53% in tests. | Makes explosions much less likely. |
The SRL blocks too much current, stopping more heat in broken batteries. | Lowers fire risk. |
Battery cell separators help your battery work well and stay safe. Shutdown separators protect you from heat dangers and make batteries safer to use every day.
Batteries often use polyolefin separator materials. The most common types are PE and PP. Both types help keep batteries safe. They react differently when they get hot.
PE separators melt at lower temperatures. They shut down at 130–140°C. PP separators stay solid until 160–165°C. This means PP separators can handle more heat before melting. The table below shows their melting points and shutdown temperatures:
Separator Type | Thermal Shutdown Temperature (°C) | Melting Point (°C) |
|---|---|---|
PE | 130–140 | 130–140 |
PP | 160–165 | 160–165 |
Pick PE separators if you want your battery to shut down fast when it gets hot. This helps stop overheating. PP separators work better in batteries that run hotter. Both types resist chemicals and are strong.
Pros and Cons:
PE separator:
Shuts down quickly for safety
Stays stable with chemicals
Does not handle high heat well
PP separator:
Melts at higher temperatures
Very strong
Slower to shut down
Tip: If your battery gets hot a lot, PP separators last longer. For normal devices, PE separators keep you safe.
Some batteries use ceramic-coated separator materials. These have a polyolefin base like PE and a ceramic layer. The ceramic coating helps the separator stay strong at high temperatures. It also stops shrinking when it gets hot.
The chart below shows how ceramic coatings change shrinkage:
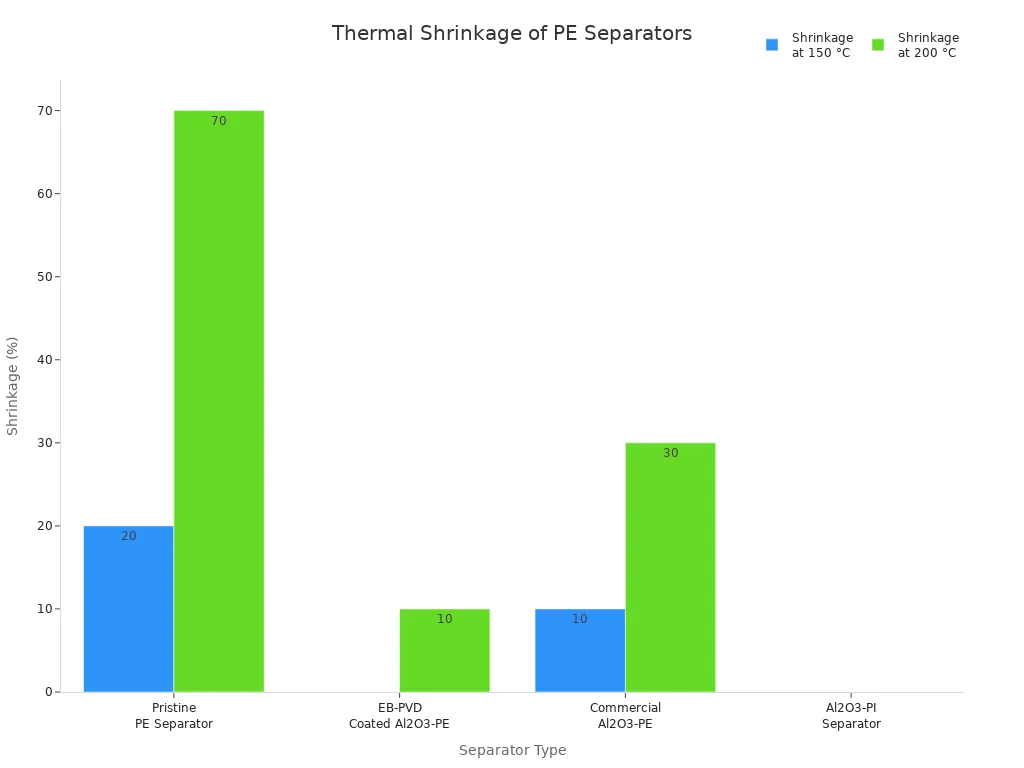
The table below compares shrinkage for different separator materials:
Separator Type | Shrinkage at 150 °C | Shrinkage at 200 °C |
|---|---|---|
Pristine PE Separator | 20% | 70% |
EB-PVD Coated Al2O3-PE | 0% | 10% |
Commercial Al2O3-PE | 10% | 30% |
Al2O3-PI Separator | 0% | 0% |
Ceramic-coated separators do not shrink at 150°C. This makes lithium-ion batteries safer. The ceramic layer also soaks up bad chemicals. This helps batteries last longer.
Pros and Cons:
Ceramic-coated separator:
Very stable at high heat
Keeps batteries safe in tough places
Makes batteries last longer
Costs more to make
Coating can come off if binder swells
PE separator:
Costs less
Shuts down well
Shrinks a lot when hot
Note: For batteries used in tough places, ceramic-coated separator materials protect best. Always check what separator your battery uses.
When you pick separator materials, think about thermal stability, strength, porosity, ionic conductivity, and chemical stability. These things help you choose the best separator for your battery.
You help keep batteries safe by knowing about separator properties. The melting point of the PE separator stops fires and short circuits. When picking a battery, look for separators that handle heat well and have lots of tiny holes. Ceramic coatings are new and make batteries safer and last longer.
Good separators protect your devices.
Better separators help batteries work longer and more reliably.
New batteries use special separators to work even better.
The PE separator sits between the electrodes. It keeps them from touching. This helps stop short circuits. The separator lets ions move through. This makes your battery work better. You get safer batteries and they last longer.
The melting point helps keep batteries safe. If the separator melts, it blocks ions. This stops the battery from working. It protects you from fires or explosions.
PE separators are used in li-ion batteries. They help keep batteries safe and steady. If it gets too hot, the separator shuts down the cell. This keeps your device safe.
A strong separator helps your battery work well. The PE separator lets ions move easily. Your battery gives steady power and lasts longer. You see fewer short circuit problems.
If the separator fails, a short circuit can happen. The electrodes might touch and get hot. Your battery could stop working or catch fire. Always use safe separator materials.